Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS), known as polythioether, polyphenyl sulfide etc., usually white or beige. The molecular structure of PPS is like this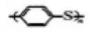 ,in which a large number of benzene rings give PPS rigidity, and a large number of thioether bonds provide flexibility, and the continuous use temperature is 200-240 ° C, and the decomposition degree is >400 ° C.
,in which a large number of benzene rings give PPS rigidity, and a large number of thioether bonds provide flexibility, and the continuous use temperature is 200-240 ° C, and the decomposition degree is >400 ° C.
Polyphenylene sulfide has a wide application. For example, fiber-reinforced polyphenylene sulfide resin can form polyphenylene sulfide fiber by way of melt-spun, which has excellent thermal stability and flame retardancy, and is mainly used for high-temperature flue gas, special heat medium filtration, and dry belt of the paper industry, cable-clad layers and fire-retardant fabrics as well as high-grade fire-fighting garments; needle-punched filter felts made of polyphenylene sulfide fibers are widely used in high-temperature flue gas dedusting filters for coal-fired boilers such as power generation, steel, cement, and waste incinerators. on. In addition, compared with high temperature resistant fibers such as polyimide fiber, polytetrafluoroethylene fiber and aramid fiber, polyphenylene sulfide fiber has the advantages of easier spinning, good spinnability and low price. It has become one of the most important high-performance thermoplastic polymer materials, maintaining a high growth rate worldwide.
Foreign research and development one step ahead
In this paper, the author uses the China Patent Abstracts Database (CNABS) as the information source. The data is as of December 20th, 2016 (public day), and 299 patent applications involving polyphenylene sulfide fiber with the classification number D01F are taken as samples.
The author found that Phillips obtained the patent of PPS synthesized from dichlorobenzene and sodium sulfide in N-methylpyrrolidone polar solvent in 1967. In 1979, it synthesized a high molecular weight linear PPS resin suitable for spinning and realized industrial production. It is reported that before 1985, Phillips has been monopolizing the production and market of PPS.
However, in just a few years after the expiration of Phillips' patents, Japanese companies have established resin and compounding processing plants. Toray, Toyobo, and Wu Yu have successively developed PPS fibers, which is the most important supplier of PPS fiber in the Chinese market currently. In 2001, Toray acquired the PPS fiber business of Phillips. Since 2005, due to the rapid increase in market demand, several companies in the US FIT, Switzerland Nexis, and China have successively joined the PPS fiber research and production lines.
Foreign research
Domestic R&D is in full swing
In China's patent application for polyphenylene sulfide fiber, 71% of patent applications were filed by domestic applicants, and the remaining 29% of patent applications were mainly for foreign applicants entering China through the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT). In the field of chemical fiber, the proportion of patent applications filed through the PCT route is greater than that of other fibers. It can be seen that in the technology of polyphenylene sulfide fiber, foreign applicants pay more attention to the Chinese market and actively carry out patent layout.
From the perspective of major applicants and applications, patent applicants entering China through the PCT route are mainly Japanese companies such as Toray and Teijin. Take Toray Corporation as an example,as a world-renowned research and development and production company of polyphenylene sulfide, its patent application is significantly higher than other companies, which shows that Japanese companies have absolute advantages in this technology field.
Among the domestic patent applicants in this technical field, the top patent related applications are research institutions or enterprises such as Donghua University, Shanghai Te Anlun, and China Textile Academy. The author found that in the 1990s, patent applications for polyphenylene sulfide fibers began to appear in China, but the growth rate of patent applications was relatively slow. However, after 2002, China’s patent applications for polyphenylene sulfide fibers have steadily increased. In addition to the two low tides in 2008 and 2011, the number of patent applications in this field in China has been increasing year by year. The author analyzed that this may be closely related to the growing recognition of the importance of polyphenylene sulfide fibers and their advantages in environmental management. It is worth noting that although domestic applicants have a certain number of patent applications in this field, the number of individual subject applications is small and relatively scattered, and needs to be further strengthened.
Improved processing is promising
The author suggests that relevant patent applicants in China may pay attention to the improvement of polyphenylene sulfide fibers in the future, such as fiber blending modification, spinning process and fiber surface treatment modification.
After searching, author found that there are many patent applications involving blending modification, which are mainly divided into two categories. One is polyphenylene sulfide and other fiber-forming polymers blended and modified, such as polyamide, polyester, polyolefin polyetherimide which can improve the spinning performance and so forth (such as the patent application disclosed in CN102898836A, CN102898837A, CN103774277A); the other is the modification of polyphenylene sulfide with other auxiliaries, which can impart anti-aging and other functions to the fiber or other improved performance. Other additives mainly include anti-aging agents, nano-functional particles and so on. The patent application disclosed in CN102839446A uses a combination of an ultraviolet absorber, a light stabilizer and an antioxidant in a polyphenylene sulfide to form a light fastness agent, which solves the problem of poor light resistance of the PPS fiber. In recent years, graphene has been used as a newly discovered carbon material for polyphenylene sulfide fibers to improve its performance. For example, the patent application disclosed in CN104894678A uses polyphenylene sulfide resin, graphene, coupling agent and Kaolin composed of polyphenylene sulfide resin mixture to make a high-strength and high-modulation polyphenylene sulfide staple fiber; the patent application with the publication number CN104894680A is made by blending polyphenylene sulfide PPS resin with graphene to obtain polyphenylene sulfide composite fiber with a good performance of strong breaking strength and aging resistance.
The improvement of the spinning process mainly lies in the setting of the spinning conditions and the modification of the fiber morphology structure. For example, the patent application with the publication number CN100999833 mainly uses melt-spinning at 280-350 °C by using linear polyphenylene sulfide with excellent performance as a raw material, and heating at a device with temperature of 250-320 ° C during the spinning proces under reasonable control of the heat preservation and cooling temperature,and the fiber winding speed is controlled at 300-1500 m / min,and the taken-up fiber is drawn at 80-280 ° C and is set at 150-300 ° C. Since the polyphenylene sulfide fiber produced by invention has high production rate, the fiber has excellent fracture strength, elongation at break, dry heat shrinkage and the like, and is particularly suitable for the production of polyphenylene sulfide filament fiber. The patent application with the publication number CN101109110A uses PPS (polyphenylene sulfide) as the skin layer and the eccentric core structure of PET (polyester), PBT, PA6 (polyamide) or PA66 (polyamide) as the core laye to spin long or short fibers.
The method of fiber surface treatment modification is usually carried out in the form of fiber surface coating or oil. The patent application disclosed in the publication No. CN102560718A is coated with a polyphenylene sulfide fiber surface treatment solution in a polyphenylene sulfide fiber, and dried to a constant weight at a room temperature of -150 ° C under normal pressure air or vacuum condition, from which the polyphenylene sulfide fiber product having a surface coating thickness of 1-5 μm anti-oxidation protective layer can be achieved.The polyphenylene sulfide fiber surface treatment liquid described in the present technology contains a solvent, an antioxidant, a film former, a coupling agent, and inorganic filler particles. Compared with the prior technology, the invention provides a preparation method of the surface-coated anti-oxypolyphenylene sulfide fiber, and the surface of the polyphenylene sulfide fiber is coated with an anti-oxidation protective layer having a certain thickness, which can not only improve the fiber's oxidation resistance but also prolong its longevity. The patent application with the publication number CN103409855A relates to a polyphenylene sulfide short fiber spinning oil agent and a preparation method thereof, wherein the weight percentage composition of the compound raw materials is 25-50% of an antistatic agent, 15-25% of a smoothing agent, 18 to 35% of a holding mixture, 5 to 20% of the emulsifier, and 2 to 8% of the conditioning agent.Because the oil agent has better antistatic property, smoothness, cohesiveness and the like, the spinning production and the post-processing process can be smoothly carried out, and the spinning effect and the mechanical properties of the fiber can meet the production requirements.
Source: China Intellectual Property News